Surgery
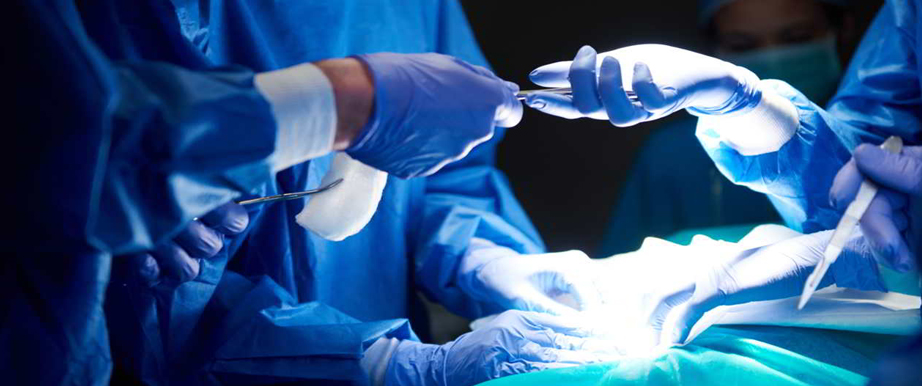
Surgery is a medical procedure that involves the physical intervention on tissues or organs to treat a medical condition. It can be used for various purposes, such as diagnosis, treatment, or palliation of diseases. Surgical procedures are usually performed by specialized doctors called surgeons and can vary in complexity, from minimally invasive to extensive operations.
Types of Surgery
- Elective Surgery: Planned in advance and is not an emergency. Examples include cosmetic surgery, joint replacements, and hernia repairs.
- Emergency Surgery: Performed immediately to save a life or prevent severe complications, such as in cases of trauma, appendicitis, or bowel obstruction.
- Diagnostic Surgery: Performed to confirm a diagnosis, such as biopsies where tissue samples are taken to be examined for diseases like cancer.
- Curative Surgery: Intended to cure a disease or condition. For example, removing a tumor or gallbladder.
- Reconstructive Surgery: Aims to restore the appearance or function of a body part, often after injury or due to birth defects. Examples include breast reconstruction after mastectomy or cleft lip repair.
- Transplant Surgery: Involves replacing a diseased organ with a healthy one from a donor, such as heart, kidney, or liver transplants.
- Palliative Surgery: Performed to relieve symptoms and improve the quality of life, often used in advanced stages of diseases like cancer to alleviate pain or obstruction, rather than to cure the condition.
- Minimally Invasive Surgery: These techniques, such as laparoscopic or robotic surgery, use smaller incisions, resulting in faster recovery times and reduced scarring. Examples include gallbladder removal and certain types of hernia repair.
Common Surgical Procedures
- Appendectomy: Removal of the appendix, usually due to appendicitis.
- Cholecystectomy: Removal of the gallbladder, often due to gallstones.
- Coronary Artery Bypass Graft (CABG): Surgery to improve blood flow to the heart by bypassing blocked arteries.
- Hip or Knee Replacement: Replacement of damaged joints with artificial ones, common in severe arthritis cases.
- Cataract Surgery: Removal of the cloudy lens from the eye and replacement with an artificial lens.
- Cesarean Section (C-section): Surgical delivery of a baby through incisions in the abdomen and uterus.
Pre-Surgery Considerations
- Preoperative Assessment: Includes blood tests, imaging, and evaluations to assess the patient's overall health and suitability for surgery.
- Anesthesia: Administered to prevent pain during surgery. Types include general anesthesia (puts you to sleep), regional anesthesia (numbs a specific area), and local anesthesia (numbs a small part of the body).
- Informed Consent: The surgeon explains the risks, benefits, and alternatives, and the patient provides consent for the procedure.
Post-Surgery Considerations
- Recovery and Rehabilitation: Depending on the type of surgery, recovery can range from a few days to several months. Rehabilitation may include physical therapy or wound care.
- Complications: Potential risks include infection, bleeding, blood clots, or adverse reactions to anesthesia. Close monitoring and follow-up care are essential to manage any complications.
Advanced Surgical Techniques
- Robotic Surgery: Surgeons control robotic arms to perform precise, minimally invasive surgeries. Common in urological, gynecological, and colorectal procedures.
- Laparoscopic Surgery: Uses small incisions and a camera to guide the surgery. Less invasive, with quicker recovery times compared to traditional open surgery.
Surgery is often a necessary and effective treatment option for many conditions, though it requires careful consideration of risks and benefits. If you're considering or preparing for surgery, it’s important to discuss all aspects with your healthcare team.
Meet Our Specialist Doctor
One of the top Hospitals in Ghatkopar.




 Click to Book Appointment & Bed
Click to Book Appointment & Bed